Struggling with organizational change? Change management models provide the frameworks you need. This article breaks down the top models, explaining how they can help you implement change smoothly and efficiently.
Key Takeaways
- Change management models provide structured frameworks that help organizations navigate transformation, address employee resistance, and ensure successful implementation.
- Key models include Lewin’s Change Management Model, the ADKAR Model, and Kotter’s 8-Step Process, each offering distinct approaches to managing organizational change effectively.
- Choosing the right change management model is vital and should align with organizational goals, the type of change, and metrics for success to facilitate a smoother transition.
Understanding Change Management Models
Change management models guide organizations through transformation by providing essential frameworks. These models help outline the steps needed to implement change successfully, manage resistance, and ensure the new ways of working become the norm. They provide structured guidance, making it easier for organizations to navigate the complexities of change.
Effective change management is crucial for achieving long-term success. Without a clear change management strategy, organizations may struggle to gain buy-in from employees and stakeholders, leading to resistance and potential failure. Reliable change management models help address challenges directly, ensuring all necessary factors are considered and employees receive support throughout the transition.
Change management models offer diverse approaches and best practices tailored to an organization’s specific needs. Focusing on people, business processes, change management tools, or systems, these models manage all aspects of change, enhancing operational effectiveness and ensuring success.
Lewin’s Change Management Model
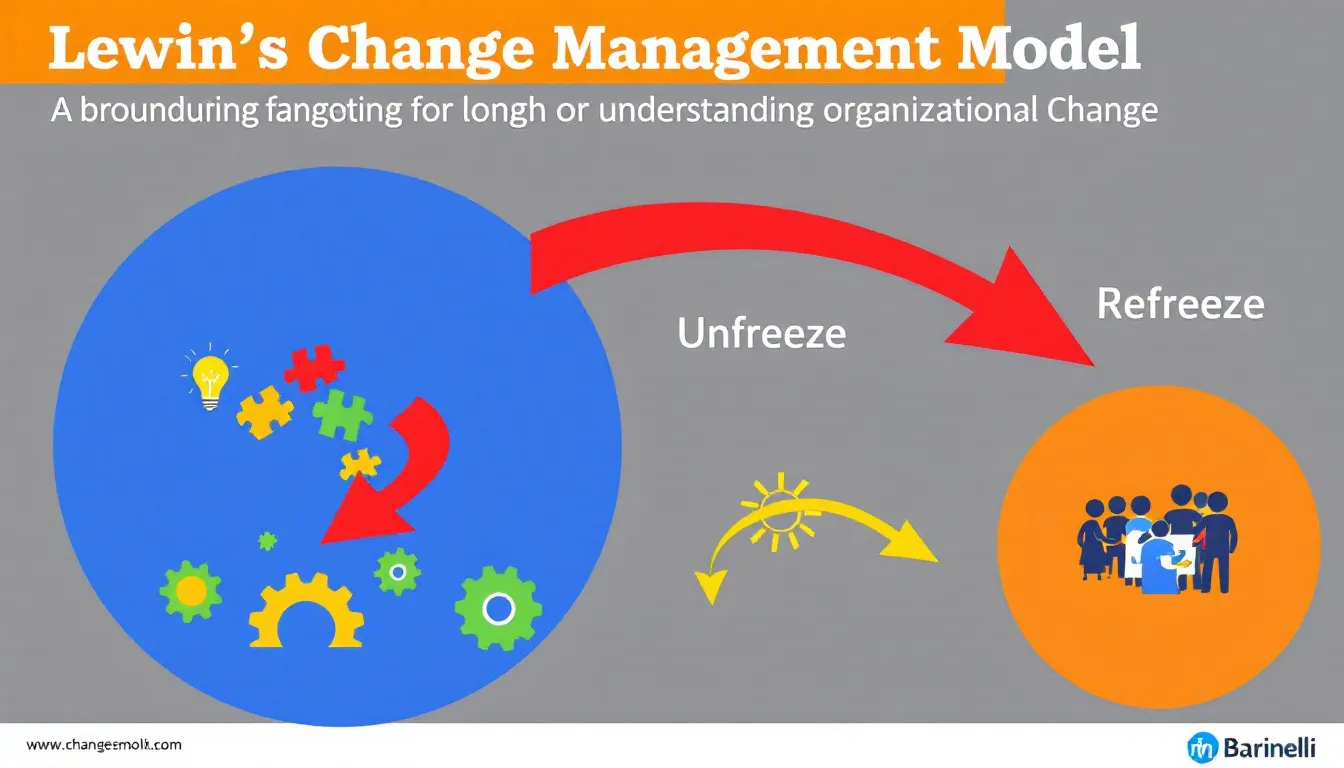
Kurt Lewin’s Change Management Model, developed in the 1950s, is one of the most popular change management models. It consists of three phases: Unfreeze, Change, and Refreeze. This model focuses on planning, preparation, and supporting employees throughout the change process.
The first phase, Unfreeze, involves preparing the organization to recognize the need for change. This critical step disrupts the current equilibrium and raises awareness about the need for change. Engaging employees and addressing concerns can reduce resistance, paving the way for a smoother transition.
The Change phase, where actual transformation occurs, requires clear communication, adequate training, and ongoing support to help employees adapt.
The Refreeze phase establishes the new status quo, ensuring changes are fully integrated and become the new norm. Lewin’s model is particularly effective for large companies as it empowers employees and avoids internal rumors, making it a reliable choice for managing organizational change.
The ADKAR Model
Created by Jeff Hiatt, the ADKAR Model is another widely used change management framework. ADKAR represents five stages for successful change: Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement. The ADKAR model emphasizes that organizational change hinges on individual change.
The first stage, Awareness, involves informing employees about the need for change, followed by Desire, where they develop a willingness to support and participate. The Knowledge stage equips employees with the necessary information and training for effective implementation.
The Ability stage ensures employees possess the skills and competencies needed for change execution. Reinforcement sustains changes over time by reinforcing new behaviors and practices. The ADKAR model is particularly useful for projects involving critical technology or process adoption, ensuring employees are well-prepared and supported.
Kotter’s 8-Step Process
Kotter’s 8-Step Process offers a comprehensive, step-by-step approach to implementing change. The first step creates a sense of urgency to motivate employees to take action and support change. This is followed by building a guiding coalition of influential individuals to lead and support the efforts.
Next, develop a strategic vision and communicate it effectively to stakeholders, creating a clear picture of the future compared to the past and the necessity of change. Business leaders must focus on short-term wins, which are crucial for maintaining momentum, providing tangible proof of progress and keeping employees engaged.
After initial successes, sustain acceleration by pursuing ongoing changes until the vision is fully realized. The final step institutes change by reinforcing new behaviors and linking them to organizational success, ensuring changes become embedded in the culture.
Kotter’s model is effective for large-scale changes, offering a clear roadmap for navigating transformation complexities.
McKinsey 7-S Framework

The McKinsey 7-S Framework is a holistic model focusing on the interconnectedness of seven key elements: Shared Values, Staff, Style, Skills, Strategy, Structure, and Systems. These elements are divided into two categories: hard elements, which are directly measurable, and soft elements, which are more culturally driven.
Particularly effective for procedural changes, this model can complement other frameworks like Kotter’s Theory and Lewin’s Model. Assessing these seven elements helps organizations identify misalignments and areas for improvement, ensuring a comprehensive approach.
A strength of the McKinsey 7-S Framework is its ability to help organizations understand the status quo and identify necessary changes. Aligning the seven elements allows organizations to create a cohesive strategy addressing both technical and cultural aspects of transformation.
Bridges’ Transition Model
Developed by William Bridges, the Transition Model focuses on the emotional journey individuals undergo during change. Unlike other models emphasizing steps, this framework distinguishes between change and transition, highlighting psychological aspects.
The model identifies three key phases: Ending, Neutral Zone, and New Beginning. The Ending phase involves letting go of old ways and dealing with associated losses. The Neutral Zone follows, a period of uncertainty and confusion where individuals are between the old and new ways. Effective communication and support during this phase are crucial to reduce anxiety and facilitate navigation.
The final phase, New Beginning, signifies a fresh start with new understandings, values, and roles established. Addressing the emotional aspects of change, Bridges’ Transition Model ensures a smoother transition and greater acceptance of new ways of working.
Nudge Theory
Popularized by Richard H. Thaler and Cass R. Sunstein, Nudge Theory promotes voluntary change through positive reinforcement and subtle guidance. Rather than enforcing strict rules, Nudge Theory encourages behavioral change by subtly altering the environment and making desired choices easier.
For example, demonstrating the benefits of a new policy can make it more appealing and easier for employees to accept. Celebrating small wins and highlighting benefits can boost participation and engagement.
Effective nudges are simple, visible, and aligned with organizational goals. Embracing Nudge Theory helps organizations avoid strict mandates and foster a more positive, supportive environment for change.
Satir Change Model
Developed by family therapist Virginia Satir, the Satir Change Model focuses on tracking employee performance throughout the change process. The model outlines five stages: Late Status Quo, Resistance, Chaos, Integration, and New Status Quo. Understanding these stages allows organizations to predict performance changes and address potential challenges.
The Late Status Quo stage represents the current state before any change. Upon introduction of change, employees may experience Resistance, leading to a dip in performance. The Chaos stage follows, with peak uncertainty and confusion. During this phase, effective communication and support are crucial for helping employees navigate the transition.
The Integration stage incorporates new ways of working and gradually improves performance. Finally, the New Status Quo stage establishes a new normal, where employees fully adapt to changes and performance stabilizes. Tracking these stages allows organizations to better manage the change process and ensure successful organizational change.
Best Practices for Implementing Change Management Models
Implementing change management models requires a structured approach for successful transitions in the change management process. Regular communication throughout the change process clarifies objectives and expectations, reducing uncertainty and resistance. Engaging employees and involving them in the process significantly improves acceptance and reduces resistance.
Creating a sense of urgency and aligning leadership support are critical for driving successful change initiatives and change initiative. Showcasing short-term successes helps eliminate resistance and maintain momentum, facilitating long-term goal achievement. Using multiple change management models together can address various aspects of transformation, offering a comprehensive approach.
Monitoring progress and adjusting based on feedback is essential for change management. Continuously evaluating the effectiveness of change initiatives and making necessary adjustments ensures successful implementation and long-term success.
How to Choose the Right Change Management Model
Selecting the right change management model is crucial for successfully guiding organizations through change. A clear understanding of change goals and their importance is necessary for successful implementation. Establishing KPIs and metrics helps determine success and track progress.
Consider the type of organizational change when selecting a change management model. Different models may suit different types of changes, such as procedural, cultural, or technological transformations. Planning, resources, attention to detail, and end-user enablement are key for effective change management.
The right change management models and tools help conquer challenges and achieve high adoption levels. Carefully selecting and implementing the appropriate model allows organizations to navigate change complexities and ensure success.
Summary
In summary, understanding and selecting the right change management model is essential for guiding organizations through successful transformations. From Lewin’s Change Management Model to Nudge Theory, each model offers unique insights and strategies for managing different aspects of change. By following best practices and continuously monitoring progress, organizations can ensure long-term success and achieve their change goals.
In conclusion, effective change management requires a thoughtful approach, clear communication, and ongoing support. By leveraging the right change management models and tools, organizations can navigate the complexities of change, overcome resistance, and achieve successful organizational change. Embrace these insights and take action to drive positive transformations in your organization.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are change management models?
Change management models are structured frameworks that assist organizations in navigating transformation, addressing resistance, and facilitating successful implementation. Utilizing these models can significantly enhance the effectiveness of change initiatives.
Why is Lewin’s Change Management Model popular?
Lewin’s Change Management Model is popular due to its emphasis on employee involvement, tackling resistance, and facilitating the complete integration of changes within the organization. This approach fosters a smoother transition and enhances overall acceptance of change.
How does the ADKAR Model ensure successful change?
The ADKAR Model ensures successful change by addressing individual stages—Awareness, Desire, Knowledge, Ability, and Reinforcement—thus preparing and supporting employees throughout the change process. This structured approach fosters a smoother transition and promotes lasting change.
What is the importance of Kotter’s 8-Step Process?
Kotter’s 8-Step Process is vital as it offers a structured framework for implementing change, focusing on creating urgency, building coalitions, celebrating short-term wins, and ensuring long-lasting momentum. This strategic approach significantly enhances the likelihood of successful organizational change.
How can organizations choose the right change management model?
To choose the right change management model, organizations should assess their change goals, establish relevant KPIs, and consider the type of change they are implementing, ensuring the selected model aligns with their specific needs. This approach will facilitate a more effective transition and successful change initiatives.
